Search results
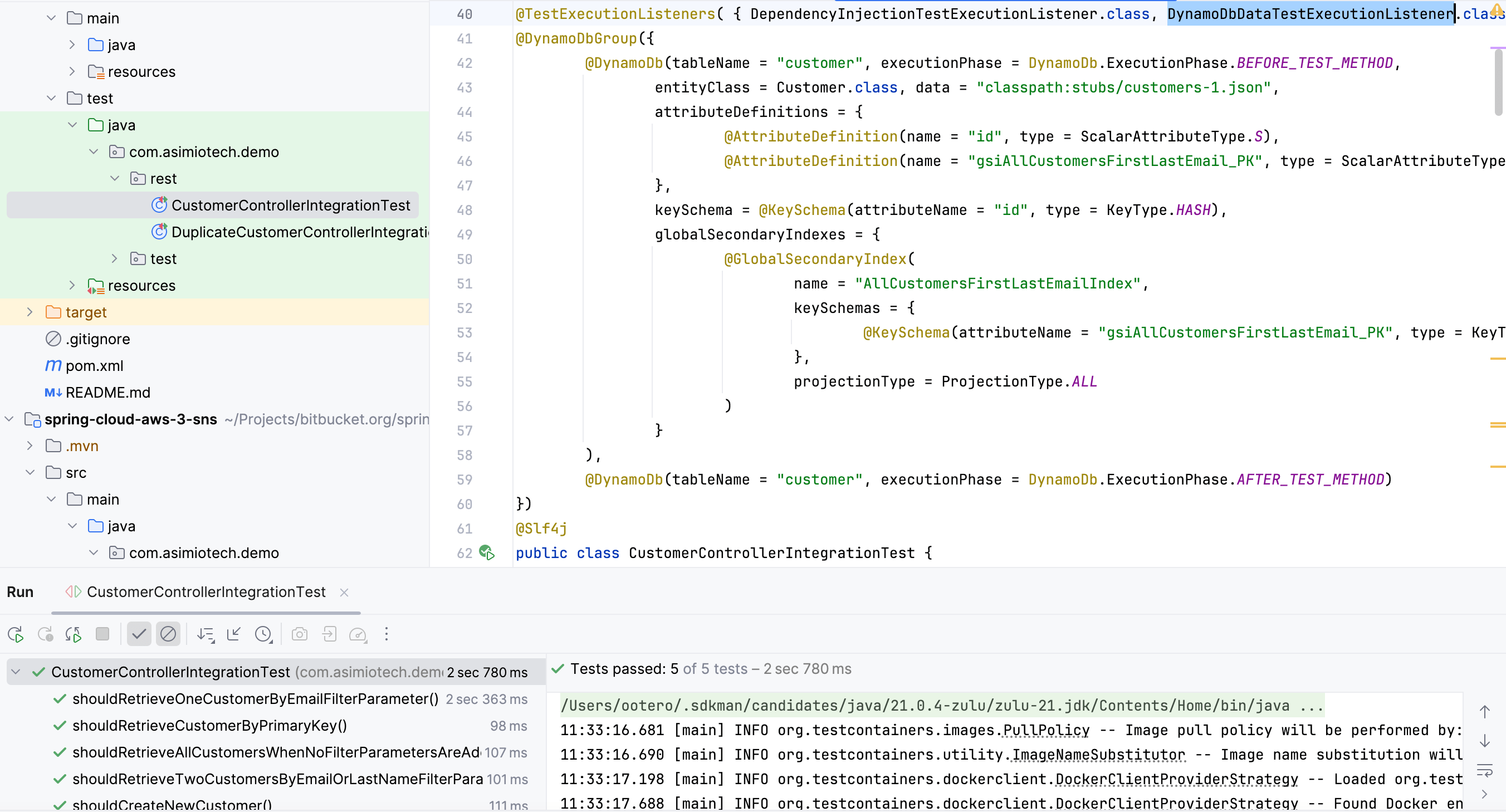
Provisioning DynamoDB tables and seeding data to run Spring Boot Integration Tests
1. OVERVIEW
You are deploying, or planning to deploy your Spring Boot RESTful applications to AWS.
Some of these Spring Boot applications might use Amazon DynamoDB data stores instead of relational databases.
Along with writing unit tests for REST controllers, business logic, etc., you should consider writing integration tests to verify the interactions between different parts of the system work well, including retrieving data from, and storing data to a NoSQL database like DynamoDB.
This blog post shows you how to write a custom Spring’s TestExecutionListener to seed data to a DynamoDB table.
Each Spring Boot integration test will run starting from a known DynamoDB table state, so that you won’t need to force the tests to run in a specific order.
Publishing AWS SNS Notifications with Spring Boot, AWS Java SDK v2, and spring-cloud-aws-starter-sns
1. OVERVIEW
Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service) is a fully managed topic-based messaging service that helps publishing notifications for subscriber/listener applications to process.
Amazon SNS follows the pub/sub model to facilitate asynchronous communication between different systems.
SNS supports multiple delivery protocols such as:
- http/https,
- email,
- sms
- AWS SQS
- AWS Lambda
- AWS Kinesis Data Firehose
- mobile applications
This blog post helps you to get started publishing notifications with Spring Boot 2 or 3, SNS, Spring Cloud AWS, and AWS Java SDK version 2, and consuming the messages via SQS with AWS CLI.

Getting started with Spring Boot, DynamoDB, AWS Java SDK v2, spring-cloud-aws-starter-dynamodb, and dynamic queries with DynamoDbTemplate
1. OVERVIEW
If your organization is working, or plans to work with large amount of unstructured data, Amazon DynamoDB would be an option to consider, especially if your organization is already invested in AWS.
DynamoDB is a schemaless NoSQL (key-value), performant, and scalable database solution.
This blog post shows you how to get started with Spring Boot 2 or 3, DynamoDB, Spring Cloud AWS, and AWS Java SDK version 2.
And continuing with the dynamic queries trend I have covered in the past when the data comes from a relational database:
- Writing dynamic SQL queries using Spring Data JPA repositories and EntityManager
- Writing dynamic SQL queries using Spring Data JPA Specification and Criteria API
- Writing dynamic SQL queries using Spring Data JPA repositories and Querydsl
as well as when the data comes from Cosmos DB:
Besides getting started, this blog post also helps you to write dynamic DynamoDB queries with DynamoDbTemplate.

Propagating Tenant data to Spawned/Async Threads with ThreadLocalTargetSource, TaskDecorator in Multi-tenant Spring Boot applications
1. OVERVIEW
In late 2017, I published a blog post about using Spring’s ThreadLocalTargetSource as an alternative to dealing explicitly with ThreadLocal in Spring Boot Multi-tenant applications.
Where did I use ThreadLocal that I found Spring’s ThreadLocalTargetSource a useful alternative?
Let’s start with some context.
Earlier that same year I had published writing multi-tenant RESTful applications with Spring Boot, JPA, Hibernate and Postgres, where I took the shared application(s), different databases, multi-tenancy approach.
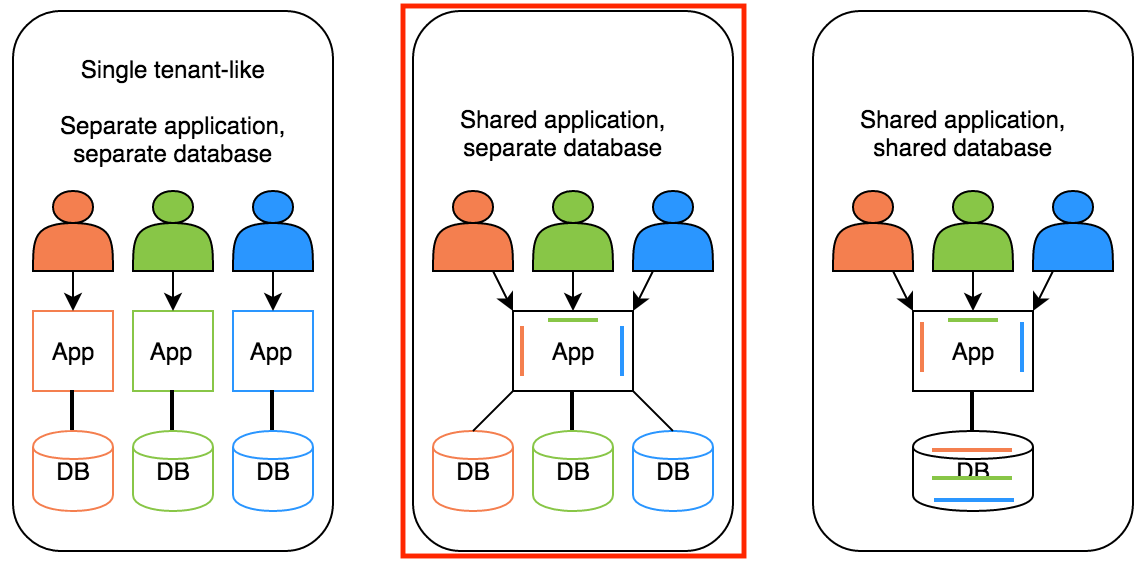 Multi-tenancy - Shared applications, different databases
Multi-tenancy - Shared applications, different databases
The implementation used an HTTP Header with the Tenant identifier to choose the relational database from which to retrieve the data from.
You could send requests like:
curl -H "X-TENANT-ID: tenant_1" http://localhost:8080/...
or
curl -H "X-TENANT-ID: tenant_2" http://localhost:8080/...
The code also included a Spring MVC Interceptor to set and clear the Tenant identifier to and from the TenantContext using that HTTP custom header.
DvdRentalMultiTenantInterceptor.java:
public class DvdRentalMultiTenantInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
String tenantId = request.getHeader(TENANT_HEADER_NAME);
DvdRentalTenantContext.setTenantId(tenantId);
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
DvdRentalTenantContext.clear();
}
}
and
DvdRentalTenantContext.java:
public class DvdRentalTenantContext {
private static final ThreadLocal<String> CONTEXT = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static void setTenantId(String tenantId) {
CONTEXT.set(tenantId);
}
public static String getTenantId() {
return CONTEXT.get();
}
public static void clear() {
CONTEXT.remove();
}
}
You can now see how the TenantContext implementation uses Java’s ThreadLocal to set, retrieve and clear Tenant’s data, through the DvdRentalMultiTenantInterceptor.
A problem with ThreadLocal is that you have to be very careful how do you use it. You’ve got to be cautions where to set/clear data to/from the ThreadLocal to prevent the tenant’s data from leaking once the thread processing the request is done and back into the pool to process a future request.
And thus how I wrote about Spring’s ThreadLocalTargetSource as an alternative to using ThreadLocal directly in Spring Boot Multi-tenant applications.
But, there was a problem:
 Multi-tenancy - ThreadLocalTargetSource and Async Requests
Multi-tenancy - ThreadLocalTargetSource and Async Requests
The Tenant identifier wasn’t being propagated when sending or processing async requests. And that’s what this blog post helps fixing.
Reuse Testcontainers initialization and configuration code with JUnit 5 Extension Callbacks in your Spring Boot Integration Tests
1. OVERVIEW
You are writing integration tests for your Spring Boot applications with Jupiter/JUnit 5 and Testcontainers.
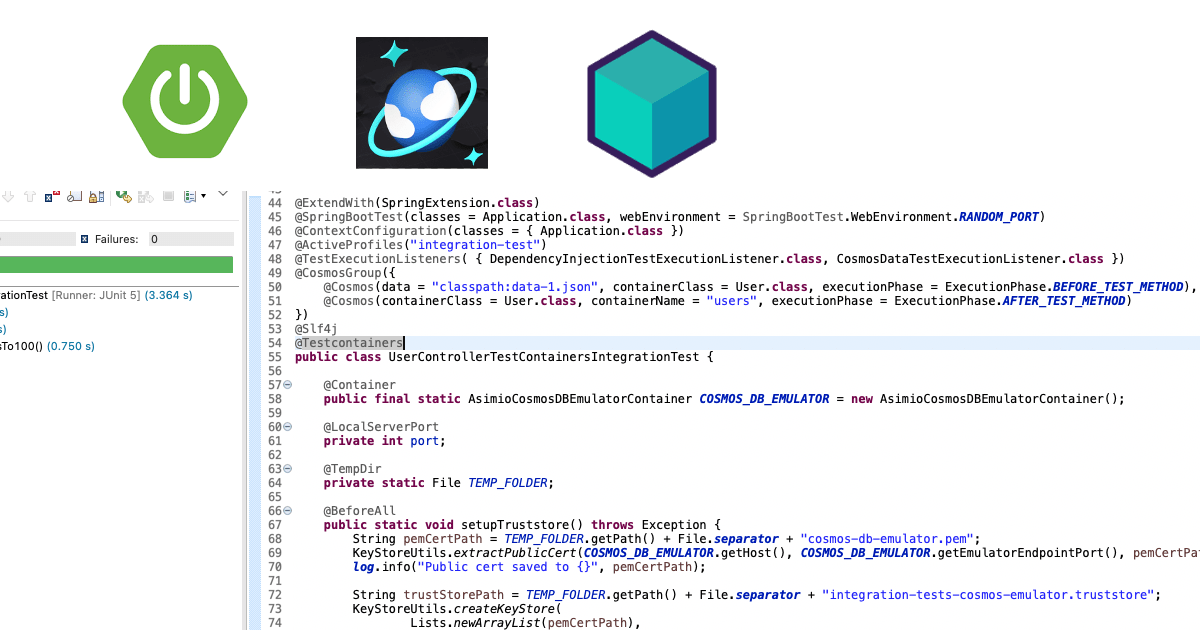
Take for instance this test class from Writing integration tests with Testcontainers and Microsoft’s Cosmos DB Docker emulator for Spring Boot applications:
UserControllerTestContainersIntegrationTest.java:
// ...
@Testcontainers
public class UserControllerTestContainersIntegrationTest {
@Container
public final static AsimioCosmosDBEmulatorContainer COSMOS_DB_EMULATOR = new AsimioCosmosDBEmulatorContainer();
@BeforeAll
public static void setupTruststore() throws Exception {
// ...
KeyStoreUtils.extractPublicCert(COSMOS_DB_EMULATOR.getHost(), COSMOS_DB_EMULATOR.getEmulatorEndpointPort(), pemCertPath);
String trustStorePath = TEMP_FOLDER.getPath() + File.separator + "integration-tests-cosmos-emulator.truststore";
KeyStoreUtils.createKeyStore(
Lists.newArrayList(pemCertPath),
trustStorePath,
"changeit"
);
System.setProperty("javax.net.ssl.trustStore", trustStorePath);
System.setProperty("javax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword", "changeit");
System.setProperty("javax.net.ssl.trustStoreType", "PKCS12");
}
@DynamicPropertySource
public static void cosmosDbProperties(DynamicPropertyRegistry registry) throws Exception {
registry.add("spring.cloud.azure.cosmos.endpoint", COSMOS_DB_EMULATOR::getEmulatorEndpoint);
}
@Test
public void shouldRetrieveUserWithIdEqualsTo100() {
// ...
}
// ...
}
The AsimioCosmosDBEmulatorContainer class extends from Testcontainers’ GenericContainer class because its instantiation and configuration got too complex and noisy.
It makes the code easier to read, maintain, while also helping you to prevent Copy and Paste code in case you need to write more Spring Boot, Cosmos DB-based integration test classes.
Also, notice the custom truststore setup for the tests to run. That’s because every time a Cosmos DB emulator Docker container starts, it generates a different self-signed certificate.
Which by the way, if your Spring Boot integration tests not only connects to a Cosmos DB emulator Docker container, but also to other Docker containers that also generate self-signed certs, you would also need to add them to the same truststore your tests use, making the testing setup even more complex.
And lastly, note the @DynamicPropertySource piece needed for the Spring Boot integration tests to know the Cosmos DB emulator endpoint’s random Host port they’ll send requests to.
Now the questions that drove me write this blog post:
- What if you need to write a couple of dozen integration tests using Testcontainers with a setup similar to the one I described above?
- How do you run only one Docker container for the tests suite to use instead of starting a new Docker container for each integration test class?
- How do you write all these Testcontainers’ instantiation and configuration code in a reusable fashion?
- How do your integration tests or Docker containers share a kind of test context (ExtensionContext in Jupiter/JUnit
5parlance) with resources they might need? For instance, a truststore that different Docker containers need to add a self-signed certificate to.
One approach to writing reusable Testcontainers instantiation and configuration code is to use Jupiter/JUnit 5 Extension Callbacks. And that’s what this blog post covers.
Writing integration tests with Testcontainers and Cosmos DB Docker emulator for Spring Boot applications
1. OVERVIEW
As part of your organization’s modernization effort, your team is writing Spring Boot applications that store data to, and retrieve data from Azure Cosmos DBs instead of relational databases.
You might have written dynamic Cosmos DB queries using Spring Data Cosmos and ReactiveCosmosTemplate.
Your integration tests might be connecting to a dedicated Cosmos DB hosted in Azure, which increases your organization’s subscription cost.
You could instead be using a dedicated Cosmos DB emulator Docker container you would need to make sure is running, and which ports it listens on, before you seed test data and run every test.
Or you might not have integration tests at all. But you also know integration testing is one of the keys to deploy often and with confidence.
This blog post shows you how to write integration tests with Testcontainers and the Cosmos DB Docker emulator for Spring Boot applications.
Listening on available ports instead of hard-coding them. And importing the Cosmos DB self-signed emulator certificate to a temporal Java truststore your tests could use.
All these automated.
Deploying Spring Boot applications from a Maven repository to Azure Spring Apps with Azure CLI
1. OVERVIEW
Azure Spring Apps is a platform as a service (PaaS) and one of the services Azure offers for your organization to run Spring Boot applications.
With very little effort, you can provision the Azure Spring Apps infrastructure required to deploy and run Spring Boot Web, RESTful, Batch, etc. applications. This allows your team to spend more time with the applications’ business logic.
This blog post covers provisioning the Azure Spring Apps infrastructure using Azure CLI to deploy a Spring Boot application previously stored in a Maven repository hosted in an Azure Blob Storage container.
Writing integration tests with GreenMail and Jsoup for Spring Boot applications that send Emails
1. OVERVIEW
Your organization implemented and deployed Spring Boot applications to send emails from Thymeleaf templates.
Let’s say they include reports with confidential content, intellectual property, or sensitive data. Is your organization testing these emails?
How would you verify these emails are being sent to the expected recipients?
How would you assert these emails include the expected data, company logo, and/or file attachments?
This blog post shows you how to write integration tests with GreenMail and Jsoup for Spring Boot applications that send emails.
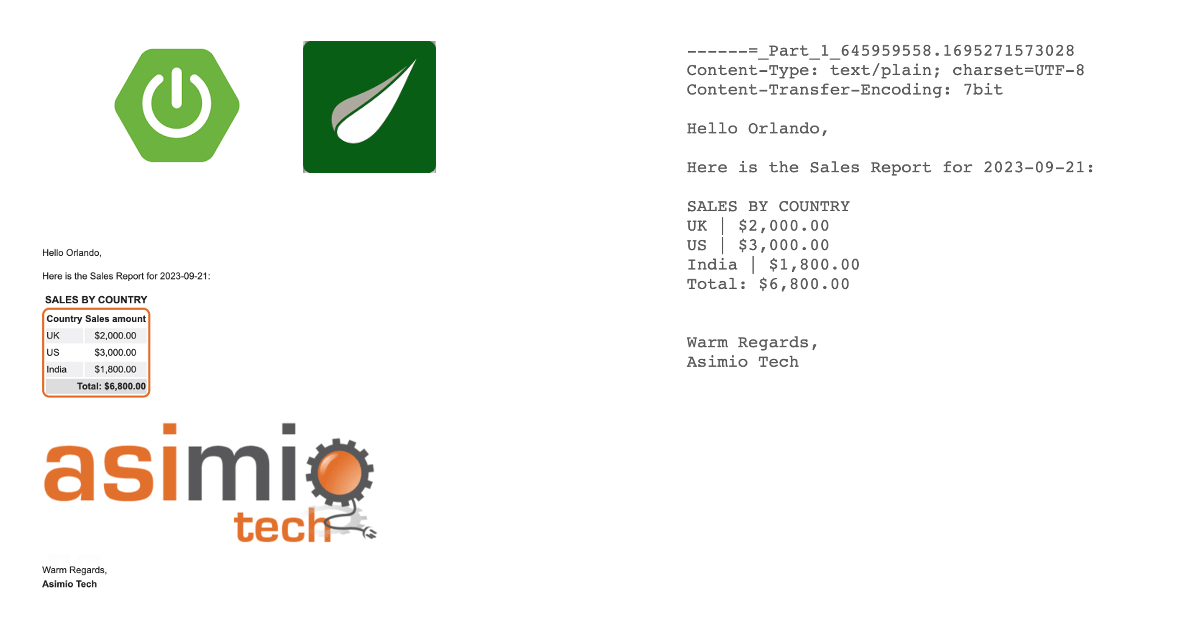
Sending Emails with Spring Boot and Thymeleaf
1. OVERVIEW
Your team used Java and Spring Boot to implement Logistics functionality, or a Hotel reservation system, or an e-commerce Shopping Cart, you name it.
Now Business folks would like to receive emails with daily shipment reports, or weekly bookings, or abandoned shopping carts.
Business people would like to get emails with consolidated data to take decisions based on these reports.
Spring Framework, specifically Spring Boot includes seamless integration with template engines to send HTML and/or text emails.
This blog post covers how to send HTML and text emails using Spring Boot and Thymeleaf template engine.
Extract Certificate and add it to a Truststore Programmatically
1. OVERVIEW
A few days ago I was working on the accompanying source code for:
-
Seeding Cosmos DB Data to run Spring Boot 2 Integration Tests
-
Writing dynamic Cosmos DB queries using Spring Data Cosmos repositories and ReactiveCosmosTemplate
blog posts, and ran into the same issue a few times.
The previously running azure-cosmos-emulator Docker container wouldn’t start.
I had to run a new azure-cosmos-emulator container, but every time I ran a new container, the emulator’s PEM-encoded certificate changed. That meant the Spring Boot application failed to start because it couldn’t connect to the Cosmos DB anymore. The SSL handshake failed.
A manual solution involved running a bash script that deletes the invalid certificate from the TrustStore, and adds a new one generated during the new Docker container start-up process.
That would be fine if you only need to use this approach once or two during the development phase.
But this manual approach won’t work for running Integration Tests as part of your CI/CD pipeline, regardless if an azure-cosmos-emulator container is already running, or if you rely on Testcontainers to run a new one.
This blog post covers how to programmatically extract an SSL certificate from a secure connection and add it to a TrustStore that you can use in your integration tests, for instance.





